Geography
Physical Geography
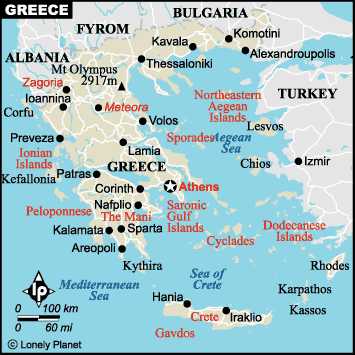
Location:
Southern Europe, bordering the Aegean Sea,
Ionian Sea,
and the Mediterranean Sea, between Albania and Turkey.
Total area:
131, 940 sq km
Land boundaries:
Total 1, 210 km, Albania 282 km, Bulgaria 494 km, Turkey 206 km
Coastline:
13, 676 km
Greek Climate
Early Greeks lived on the outskirts of the land,
always wanting to be as close to water as possible in
order to make transportation and fishing easier.
Because of this, they may have had a more constant climate
that they would have inland. This is due to the cooling properties
of water and land. Land (as with almost any solid surface) cools faster
than a liquid such as water. So around the water you receive a very
softened climate. Water heats up slower and cools slower. A solid
object on the other hand heats quicker and cools quicker.
Mountain regions in Greece as in any place have different climates
from the places which surround them. As altitude increases it is like going
up in latitude. It generally tends to get cooler. This cool air causes
the air forced up over the mountain to cool also, causing it to lose its
ability to hold its water. This causes the water to either fall out in the
form of rain or (if cool enough) snow. This snow is important because it
supplies the streams and rivers.Rain, while sufficent, was not ample to produce grain crops.
Cities
